An obesogenic diet may cause inheritable epigenetic changes. Learn more about the possible impact of an obesogenic diet on future generations.
In this article:
- What is Pterostilbene?
- Resveratrol vs Pterostilbene
- Pterostilbene and Cancer
- Pterostilbene and Cardiovascular Health
- Pterostilbene Effects on Diabetes
- The Future of Pterostilbene
What is Pterostilbene?
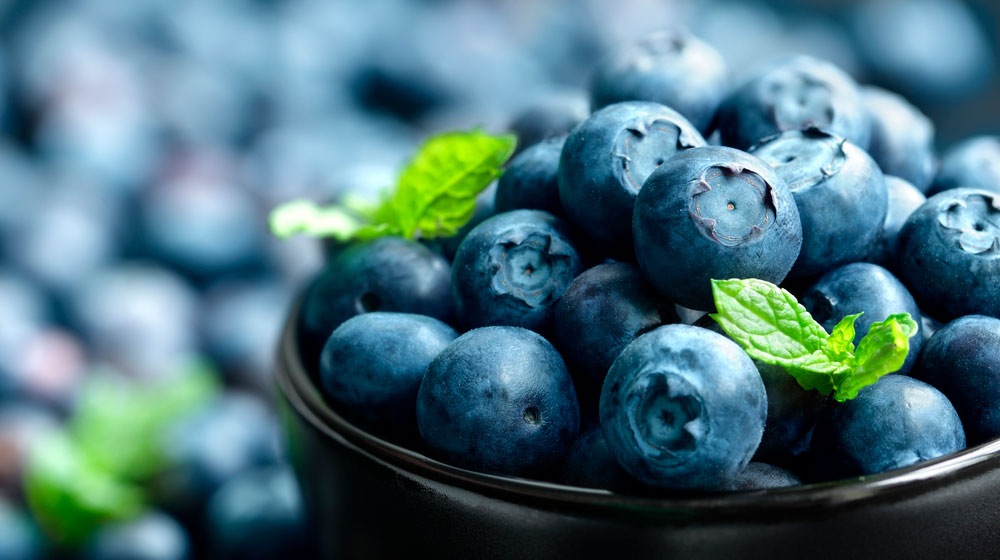
Pterostilbene (Pronounced tear-oh-STILL-bean) is a potent polyphenol, a type of chemical that occurs in plants, particularly blueberries.
What is a polyphenol? A compound with a particular chemical structure, consisting of multiple phenolic hydroxyl groups. Polyphenols protect plants by fighting harmful microorganisms. In humans, it may work as an antioxidant.
It may have the potential to prevent and treat a variety of diseases. The therapeutic potential might be because of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic properties leading to improved function of cells and repression of harmful cell growth.
Similar to other polyphenols, researchers don’t fully understand pterostilbene works. However, it has a complicated effect on antioxidant activity and may affect the way diseases develop. What’s more, it seems tailored to correct aberrant cells for different illnesses. For example, it may cause programmed cell death in cancer but has the opposite effect in the vascular system.
In short, this potent compound may affect multiple organ systems in unique ways, including:
- Protecting neurological function
- Inhibiting malignant tumor growth
- Protecting against hemolysis and liver disease
- Regulating metabolism
- Improving diabetes
- Reducing vascular diseases
Additionally, it appears to have a synergistic effect on certain medications.
Resveratrol vs Pterostilbene
Resveratrol is a polyphenol found in grapes that uniquely affect yeast. Additionally, it appeared to cause gene expression changes.
Research on pterostilbene is still ten years behind resveratrol, but it may be more beneficial.
First, resveratrol has three hydroxyl groups, which means it’s eliminated from the body quickly. Pterostilbene only has one, and it’s structure allows it to cross cell membranes easier, making it more bioavailable than resveratrol. It has 80% bioavailability, compared to 20% for resveratrol. In other words, pterostilbene stays in the body longer and therefore applies its benefits for longer.
In 2003 resveratrol seemed to be the most promising polyphenol, but it hasn’t lived up to the hype. While the benefits of both polyphenols are the same, pterostilbene is more powerful.
Pterostilbene and Cancer
Some evidence suggests pterostilbene may help prevent and treat certain types of cancer, including:
- Breast
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Colon
- Prostate
While the exact mechanism is still unknown, researchers think the antioxidant effect may be the main reason behind its anti-cancer properties.
Pterostilbene affects various critical cancer pathways. First, it reduces the multiplication of cancer cells and prevents secondary tumors from developing. It also alters the cell cycle and induces programmed cell death.
Obesity and poor nutrition are major contributors to breast cancer rates in women. Several studies have shown blueberry extract may slow down breast cancer growth. Additionally, it may alter cellular oxidative activity, which contributes to pterostilbene-mediated cell death.
Furthermore, it may increase the inhibitory effect of the chemotherapy drug, Tamoxifen, displaying potential in breast cancer treatment.
In a study, researchers found a blueberry diet may protect rats against esophagus cancer. After eating blueberries for 35 weeks, the rats had fewer tumors and showed a decreased expression for specific inflammatory markers.
Studies have also found that blueberry juice may prevent cancerous gastric cells from growing. Additionally, it reduces gastrointestinal inflammation, which may lower an individual’s risk of developing colon cancer.
Pterostilbene and Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S. It has multiple risk factors such as smoking, diet, and an inactive lifestyle.
On a cellular level, mechanical and oxidative stress causes the interior surface of arteries to become damaged. Antioxidants may have a protective effect on arteries by reducing oxidative stress.
Routinely consuming antioxidant-rich food may reduce the risk of heart disease. Some studies found the effect of blueberries and pterostilbene particularly beneficial to prevent heart disease.
Separate studies show it may hinder programmed cells death and destroy damaged cells. In other words, it may help the body get rid of abnormal proteins and counteract the effects of free radicals.
Pterostilbene Effects on Diabetes
The rate of diabetes has increased dramatically over the last few decades because of obesity and inactive lifestyles. While lifestyle changes may improve diabetes, medication is often necessary. Unfortunately, diabetes medications may have significant side effects.
In one study, rats consuming a high-fructose diet combined with pterostilbene-rich heartwood had lower insulin and glucose levels. Furthermore, researchers found oral dosing of pterostilbene decreased plasma glucose levels by 42% and body weight by 20%.
Moreover, researchers think the antidiabetic properties may reduce oxidative stress, increase antioxidant activity, and lower the impact of free radicals on kidney and liver cells.
The Future of Pterostilbene
As mentioned earlier, pterostilbene research is relatively new, but more benefits are likely to be discovered in the future.
Most importantly, it’s a sirtuin-activating compound. Sirtuins are proteins that regulate cellular health. Consequently, uncovering how this compound works can have a massive impact on the way we treat diseases in the future.
To sum up, pterostilbene, like other polyphenols, may have many benefits and contribute to the treatment and prevention of certain diseases. Because of its structure and bioavailability, it may be more potent than other polyphenols like resveratrol. Studies show it’s particularly beneficial as an antioxidant that protects against diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. While animal studies have shown positive results, it’s still relatively new, and human studies may shed more light on this powerful compound.
Surprised by these findings? Share your thoughts in the comment section below!
Or, check out our other blogs to explore recent Epigenetic research.